In this article I want to explain you about what is it Technical SEO. When we hear the term “technical,” we often tend to think of programming languages or things related to coding. In fact, that’s partly true, but don’t worry. If you’re a beginner or company without a specialized SEO in house , this guide will cover the basic aspects so you can understand easily and start applying them to your website.
Table of Contents
What Do We Mean by Technical SEO?
Technical SEO is one of the main pillars of an SEO strategy and focuses on optimizing aspects related to a website’s visibility. That is, making it easier for all the “important” business/core/services pages of a site to be crawlable and indexable, giving them the chance to appear in search engines.
Examples of Technical SEO actions:
- Optimizing website loading speed
- Optimizing indexation
- Optimizing website architecture
- Mobile optimization
- ….
1. Understanding Crawling
What is crawling?
Crawling is the process by which search engines explore and collect information from different websites, whether it’s new or updated content. This process is carried out by the well-known “spiders” or “bots” that browse the web by following links from one page to another.
When a spider finds a new website or a new page, it analyzes its content and follows both internal and external links to discover additional pages. It’s important to ensure that all the main pages of your website are accessible to these bots so that they can properly index your site’s pages later.
How does crawling work?
URL Sources
The first step for a crawler is to create a list of URLs it finds through links on web pages. Another method they use to discover more URLs is through sitemaps.
Crawl Queue
URLs that need to be crawled or re-crawled are prioritized and added to this crawl queue (a list ordered by priority of URLs that Google wants to crawl).
Crawler
This is a system that gathers the content found on web pages.
Processing System
Multiple systems handle canonicalization. These systems direct pages to the renderer, which loads the page content similarly to a browser and processes it to find more URLs that can be crawled.
Renderer
Its function is to load a page like a browser would, using JavaScript and CSS, so Google can view the content as most users would.
Index
The stored pages that Google shows to users.
2. Understanding Indexing
What is indexing?
Indexing refers to the process by which search engines organize and store the information collected during crawling. Once a page has been crawled, the search engine analyzes it and stores it in its index—a massive database containing information about all the web pages it has discovered.
During the indexing process, the search engine evaluates the page’s content as well as other factors, such as the site’s relevance and authority, to determine where the page will appear in search results for specific user queries.
How Can You Ensure Your Pages Are Indexed?
Directives: Robots Meta Tags
This meta tag is a piece of HTML code used to tell crawlers whether or not they can index a page, and whether they should follow the links on that page and continue indexing. The robots meta tag is placed within the <head> section of a web page and looks like this:
<meta name=”robots” content=”index,follow”>
Recommendations: Canonical Attribute
When there are pages with duplicate or very similar content—that is, different versions of the same page— Google may automatically choose the version it thinks is best to show in search results. However, this may not always be the version you want indexed.
For this reason, the canonical tag is used to specify the main version of the page. The canonical tag is typically placed within the HTML of a webpage inside the <head> section and has the following format:
<link rel=”canonical” href=”exampleurl.com”>
3. Practical Technical SEO Recommendations
How to Check a Website’s Indexing
To check how many pages of your website are indexed or how they have been indexed, we recommend using the Google Search Console tool.
Internal Linking
Internal links are links from one page on your site to another page within your website. A properly implemented link juice strategy can help your pages be discovered more easily and can also contribute to improving their rankings.
The Use of Structured Data
Structured data is simply code that provides information about the content of a web page. Google mainly uses this data to better understand the page’s content.
4. Additional Technical Concepts
Below are some factors that may be less well-known but are also relevant for improving user experience.
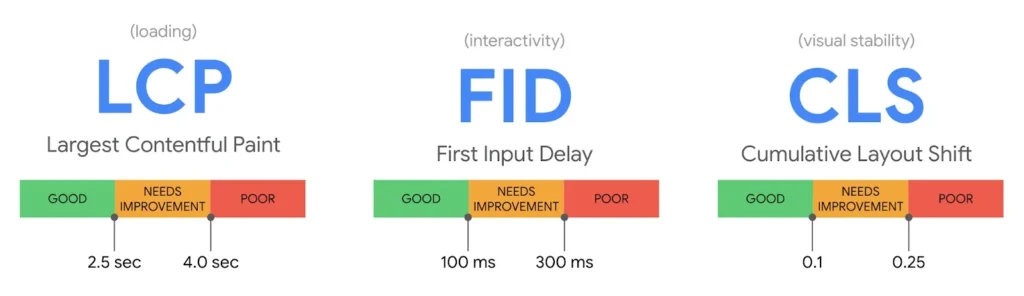
Core Web Vitals
Google’s Core Web Vitals, also known as Main Web Metrics, are indicators used to measure the real user experience when navigating a web page. They essentially focus on load time, interactivity, and visual stability.
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP):
Measures the loading performance of a website. According to Google’s recommendations, for optimal performance, LCP should be under 2.5 seconds. - First Input Delay (FID):
Measures interactivity or page responsiveness. It is the time from when a user performs an action (e.g., a click) to when the browser responds. For a good user experience, FID should be less than 100 milliseconds. - Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS):
Measures visual stability. To provide a good user experience, the CLS value should aim to stay below 0.1.
HTTPS Protocol
The HTTPS Protocol (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure) is used to transfer data securely. In other words, it protects the communication between your browser and the server from being intercepted by third parties with malicious intent, providing confidentiality, authenticity, and security to most network traffic.
Mobile Optimization
Why is mobile device optimization so important?
Having a website optimized for mobile is essential for online presence. Basically, it means checking if the pages on your website properly adapt and are easy to use for visitors accessing them from mobile devices.
To check if your website is optimized for mobile devices, simply go to the “Mobile Usability” report in Google Search Console (GSC).
There are many more concepts that can be worked on, but they require a more advanced focus. In the future, we will prepare a more advanced technical guide where we will explain additional components that can influence a website’s Technical SEO.
- OpenAI Adds Shopping Features to ChatGPT: Here’s Everything You Need to Know - May 10, 2025
- How to Create SEO-Friendly URLs - March 27, 2025
- What Are Hreflang Tag Attributes and How Can I Help You to Implement Them Correctly - March 26, 2025

One Comment